3D food printing is a process that utilizes 3D printer technology to create edible products and meals from raw ingredients like chocolates, cheese, doughs, gels, or even pureed fruits and vegetables. It works by layering the food materials to create a 3D shape. There are a variety of printing techniques but the overall process is similar to how a traditional 3D printing works only it uses food instead of plastic or other materials.
3D printing gives chefs the opportunity to manipulate basic ingredients into complex shapes that can be customized for specific dietary requirements such as low-calorie, gluten-free, lactose-free and vegan items. The printed materials are not limited by traditional forms like slicing or molding – instead they can produce intricate designs that provide an aesthetic appeal while also allowing customers with dietary restrictions to enjoy custom meals without compromising their nutrition goals. For example, a person with a gluten allergy could have a pastry made with gluten-free dough, while a person with diabetes could have a dessert made with a sugar substitute.
Another advantage of 3D food printing is its ability to reduce food waste by allowing chefs to create precise portions and designs, without having to make large batches of food that may not be sold or consumed. Additionally, 3D food printing could also be used to create more sustainable and efficient food production methods, such as using plant-based or lab-grown ingredients.
3D food printing is just starting to be used in a variety of applications, including in restaurants, hospitals, and even space exploration. For example, NASA has been working on developing 3D food printers to create sustainable food options for long-duration space missions. However, there are some obstacles that may keep the technology from going mainstream.
One of the biggest challenges is developing food-grade materials that can withstand the high temperatures and pressure of 3D printing and there are concerns about the safety and sanitation of 3D printed food. Also as well as the cost of the technology. While the cost of 3D food printing varies depending on the type of printer, materials, and other factors, it is generally more expensive than traditional methods of food production. For example, a typical 3D printer for food costs between $2,000 and $10,000. and the cost of materials such as edible inks and molds add even more to the overall cost.
For organizations willing to make the investment it may be worth the expense as 3D printed foods can be produced faster with less labor and waste compared to other methods. Additionally, 3D printing allows for greater customization of foods – from their design to their nutritional content – which is not possible with traditional techniques.
One popular example of 3D printed food is the “cake printer” which allows users to design and print their own custom cake creations. The printer works by using an edible ink cartridge to lay down thin layers of cake batter into the desired shape. Once the cake is baked, it can be decorated with frosting and other decorations.
Another example of 3D printed food is pasta. Using a specialized pasta printer, users can create intricate shapes and designs out of different types of dough. The dough is then cooked and served as traditional pasta dishes such as spaghetti or ravioli. There are even some machines that can print in multiple colors and flavors, allowing for custom creations that look as good as they taste. The technology is still in its infancy but has already been used in high-end restaurants and bakeries around the world to create unique dishes.
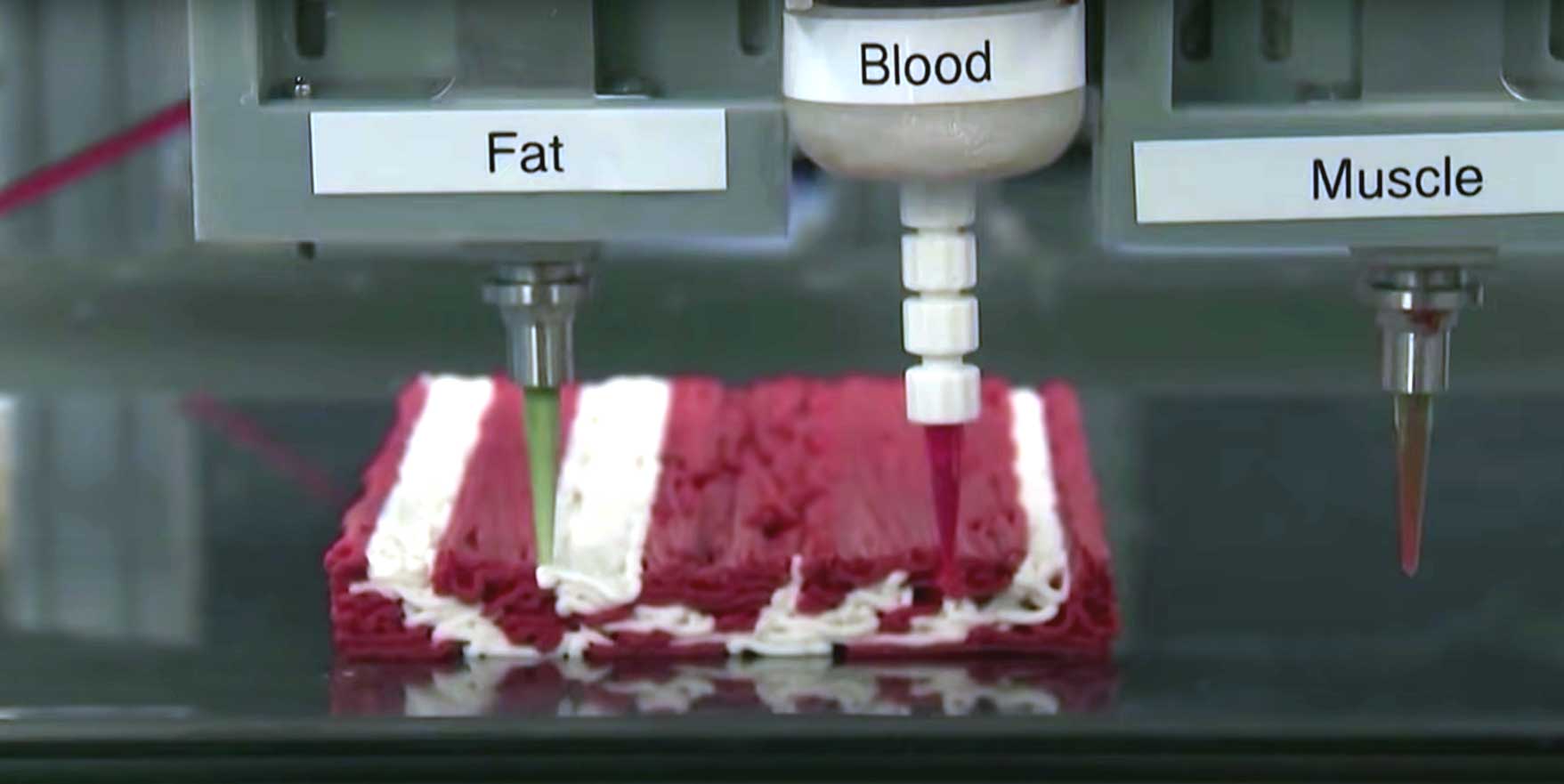
In Europe there are companies that are working on 3D printing steaks and other meats. These companies use a variety of techniques, such as layering plant-based or lab-grown meat alternatives, to create a 3D printed steak. One of the main goals of is to create a more sustainable and efficient method of meat production that can reduce the environmental impact of traditional livestock farming.
One of the companies that are working on 3D printed meat is called “Redefine Meat”, They use 3D printing technology to create plant-based steaks that have the same texture and taste as traditional meat. They use a food-grade extruder to layer plant-based ingredients, such as pea protein, together to create a meat-like structure.